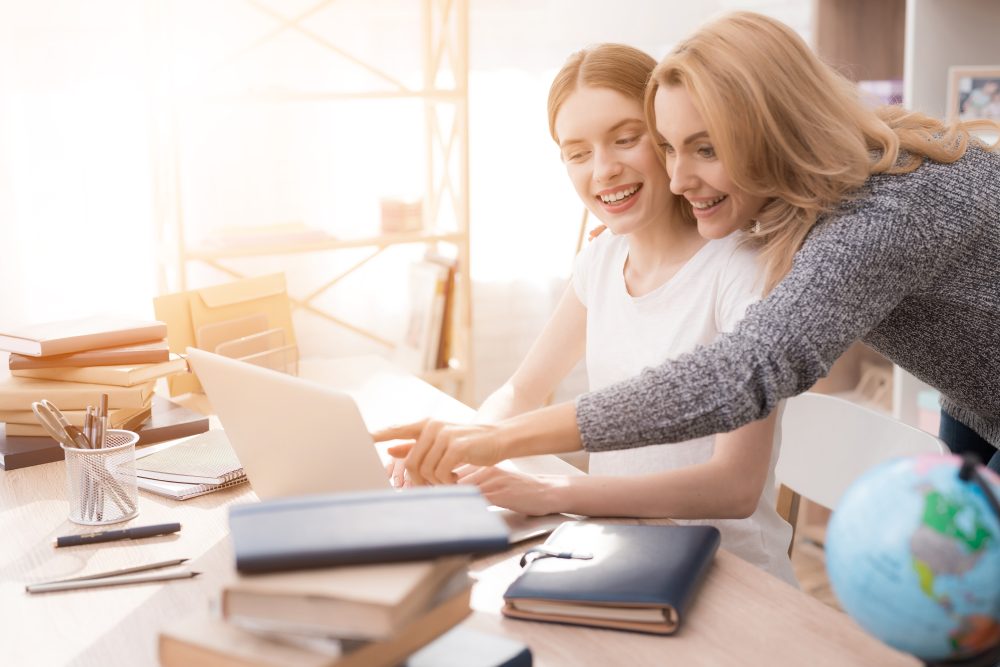
The spectre of exam season is looming, with IB, GCSE and A-levels all slated to kick off in May… and some International Baccalaureate examinations pencilled in for the very last week in April.
For teenagers facing these gateway examinations, this means it’s time to start revising – but how can parents help their children to get, or stay, motivated for revision without being perceived as the enemy? Conflict between parents and teenagers regarding schoolwork is common, says Nesma Luqman, Clinical Psychologist, Priory Wellbeing Centre, Abu Dhabi:
“The root causes are often different expectations and priorities. Parents may prioritise academic success, while teenagers may prioritise social activities. This conflict can lead to teenagers becoming defiant or disengaged, worsening tension within the family.”
The secret is to get inside the teenage brain, say psychologists. Mohamad Naamani, Clinical Psychologist, Priory Wellbeing Centre, Abu Dhabi. Mr Naamani explained to SchoolsCompared:
“The teenage brain is in flux.
The prefrontal cortex, the part of the brain responsible for planning, reasoning, and decision-making, is still developing during adolescence.
Teenagers thus tend to be more focused on short-term goals and instant gratification.
As a result, some teenagers may struggle to understand the long-term benefits of studying – and may find it difficult to motivate themselves to revise.”
The news is not all doom and gloom however. By understanding the unique features of the adolescent brain, parents can identify techniques that are more likely to be effective – and avoid the ones that are likely to be counterproductive, or cause tension, in your own parent-child relationship.
In her book ‘The Incredible Teenage Brain’, neuropsychologist Dr Jane Gilmour and her colleagues pinpoint key features of the developing teenage brain that make it very different from the brains of younger children or adults. This includes:
- A need by teenagers for autonomy – to feel that they are in charge of their own destiny rather than its being imposed on them by schools or parents;
- A keen interest in their peers – to define role models they tend to look to what their friends are doing;
- An interest in how others perceive them – they want to both fit in and be perceived positively; as well as,
- Pursuing novelty-seeking and/or risk-taking behaviour.
While these all chime with the stereotypes we might have of teenagers, it’s important to realise that these are all important, defined, and predictable steps in the developmental process of your child’s brain; they are not in control of them, and they are necessary building blocks on the journey towards shaping the brain they will have as adults. However, it is also worth noting that, being at such a crucial stage of development, also makes teenage brains particularly vulnerable to negative life experiences.
So, how can we harness this knowledge and help to safeguard and motivate teens in the context of exam revision? Here are some tips of what to do (and what not to do) to help your teen revise…
Have high expectations
There’s a big difference between unhelpful pressure and helpful expectations.
Teens need adults around them who believe in them and have high expectations of them and their ability to do well. Dr Gilmour refers to a scientific study in which students who were given notes on an essay in either a ‘wise’ tone (‘I’m giving you these comments because I have very high expectations and I know that you can reach them’) rather than a neutral tone (‘I’m giving you these comments so that you’ll have feedback on your paper’) were more than 50 per cent more likely to review and improve their essay. Dr Gilmour, also found that:
“[…] over a year later there were significantly fewer discipline problems for that same group of students. Changing a few words can impact significantly on the message received by adolescents and they will look for clues as to whether you believe they can do it.”
Don’t use threats
Constantly emphasizing negative consequences can lead to feelings of anxiety, fear, and low confidence, which can have the opposite effect on teenagers’ study habits and motivation to study, says Mohamad Naamani, Clinical Psychologist, Priory Wellbeing Centre, Abu Dhabi:
“Fear-based messages are in fact less effective in motivating people to take action. While it’s important to highlight the possible disadvantages or consequences of not revising, it’s even more important to focus on the benefits of studying (e.g., personal growth, increased knowledge and skills).
Thus, it’s important to approach discussions about revision/studying in a non-judgmental and supportive manner.
Parents should therefore refrain from using threats or harsh language, as this may create a negative and unsupportive environment for the teenager and in turn discourage them from studying.”
Be a consultant, not a micromanager
While it might be tempting to ‘help’ by drawing up a revision schedule for your teenager and making sure they stick to it, this doesn’t teach them anything – and it’s more likely to backfire in the long run. “Address their need for autonomy by playing a consultative role, not telling them what to do,” said Dr Gilmour. Coach your child to write his or her own realistic revision timetable, with regular breaks scheduled in to provide motivation. This way they are more likely to stick to it and they remain in control – something the teenage brain craves.
Harness their need to see friends
Teenagers are programmed to want to spend time with their peers, so use this need to work with you, not against you. Create some variety in their revision schedule by arranging a regular study group, where their friends come over to work and you provide the snacks. If this isn’t practical, there are many apps and websites where students can study collaboratively, or even study live with peers online – just be sure to check the security of any websites they might be using to make sure you’re comfortable with it. Read about our selection of different study apps to help teens with revision here.
Inject some novelty into the repetition
We learn through repetition, so there’s no getting away from the fact that revision is going to be a bit ‘samey’. But the adolescent brain is hardwired to seek novelty – so give it to them in the form of a new study spaces. Take them out to a café or shared working office occasionally, rearrange their desk set-up, or encourage them to take their laptop outside for a change (studies show that nature may promote learning by improving learners’ attention, levels of stress, self-discipline, interest and enjoyment in learning).
Encourage positivity
“Encouraging a teenager to revise can be challenging, but parents can support their learning by setting clear expectations, creating a study-friendly environment, helping with time management, offering guidance and support, and celebrating achievements, “ says Nesma Luqman, Clinical Psychologist, Priory Wellbeing Centre, Abu Dhabi. “It’s important for parents to be positive and avoid negative approaches, instead creating an environment that encourages their teenager to take ownership of their learning and develop intrinsic motivation.”
Never compare
Resist the urge to compare your teenager’s revision progress or academic attainment with that of friends or siblings – either favourably or unfavourably. While this might put pressure on them, it’s unlikely to truly motivate them and is more likely to chip away at their self-confidence and undermine their sense of connection with you. The focus should always be on their own growth, not how they fare in comparison to other.
Be wary of bribery
Parents often incentivise their teenagers with money or treats to encourage them to revise, but this can create a dependency on external validation and harm their intrinsic motivation, says Nesma Luqman, Clinical Psychologist, Priory Wellbeing Centre, Abu Dhabi :
“It can also damage the parent-child relationship. However, external rewards can be useful in creating good study habits and recognising achievements when used consistently, fairly, and presented as positive reinforcement. It is important to be mindful of their presentation and to promote intrinsic motivation and a healthy attitude towards learning.
Intrinsic motivation means doing something because it is inherently interesting or enjoyable, rather than because you will receive an external reward or avoid punishment. When teenagers are intrinsically motivated to learn, they are more likely to engage in deep learning and retain knowledge in the long term. Additionally, intrinsic motivation is associated with positive emotional experiences and a greater sense of autonomy and competence.
To promote intrinsic motivation, parents can encourage their teenagers to find meaning in what they are learning, connect it to their interests and goals, and provide opportunities for autonomy and self-directed learning. Parents can also model a positive attitude towards learning and demonstrate how it can be enjoyable and rewarding in itself.”
Teach them to embrace stress
Dr Gilmour states that stress doesn’t always have to be negative, and that studies show that reframing stress can make participants’ experience of a stressful event more positive. “Model a ‘stress-embracing’ perspective around the family when you feel nervous before an event, for example, and talk about it in these terms. It’s important to remember that brief periods of stress are very different from chronic stress which is feeling overwhelmed day after day – this type of stress is toxic for the developing brain.”
Check your own anxieties before projecting them on to your teen
Often our own anxieties about our teenagers’ academic progress and its impact on their future can affect the way we react. But this is not what your teen needs: they need a stable, calm pillar of support and encouragement, not a source of panic and pressure that is having a hard time with stress themselves. Talk through your own worries with your spouse, friend or therapist, and then put them to one side, so that you can be fully present for your child.
What to say to your teen
Mohamad Naamani, Clinical Psychologist, Priory Wellbeing Centre, Abu Dhabi suggests the following phrases that parents can use to motivate their children:
- “You can do this!” – This can be very motivating and reminds your children that you believe in them and their capabilities.
- “I’m proud of you for trying” – This suggests that you are acknowledging their efforts and can help build their self-esteem and motivate them to keep going.
Some strategies include:
- Teens might need to be taught revision strategies. Help them to the work into manageable tasks/chunks, as it can make the assignment feel more achievable.
- Reducing emphasis on perfection and focusing on their progress instead. Celebrate their wins, even if that means simply doing the revision itself.
- Encouraging them to use positive affirmations, such as “I am able to get this done” or “If I put in the effort, I will get the outcome I want.”
- Reward them every time they complete a planned revision. For example, you can offer a reward for every specific number of revisions/tasks completed. The number of revisions should depend on your child’s abilities and should be collaboratively decided on together with your child.
Feeling frustrated? Do this first
If you find your efforts are backfiring and you and y our teen are at each other’s throats, Mohamad Naamani, Clinical Psychologist, Priory Wellbeing Centre, Abu Dhabi suggests the following:
- Take a step back and try to understand their perspective and what might be driving their behaviour. Understanding the root of their behaviour can help you respond in a more constructive manner.
- Encourage them to share their feelings and thoughts, as communication can help develop your relationship with them. Create a safe and non-judgmental space for them to talk about their goals and interests and collaborate with them to find ways to connect with them around these areas.
- Set realistic and clear expectations and boundaries around schoolwork and revision time. However, be open to their suggestions if they feel your expectations and rules are overwhelming, and collaborate with them in creating new ones and a plan to help them meet these expectations.
- Seek external support if necessary. Sometimes, teenagers might struggle with mental health issues, academic difficulties, and other emotional/behavioural/academic-related challenges that might be too difficult for you to address alone. School counsellors, mental health professionals, special educators, tutors, etc. can offer additional support for both your teenager and yourself.
- Practice patience, as change takes time and your teenagers might not show results immediately or overnight. Provide as much support as you can and celebrate even the slightest observable progress. Even if they don’t show any progress during the beginning stages, always acknowledge their efforts and reassure them that you are available to help.
Read more about study secret to exam success here and how to get out of an exam revision rut here.
Further help
If you find yourself struggling, why not post to other parents on our Parents United Group and forum. You can meet up with other parents and post your questions here.
© SchoolsCompared.com. A WhichMedia Group publication. 2023 – 2024. All rights reserved.







































































Leave a Response